Is ASOS (LON:ASC) A Risky Investment?

Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We note that ASOS Plc (LON:ASC) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for ASOS
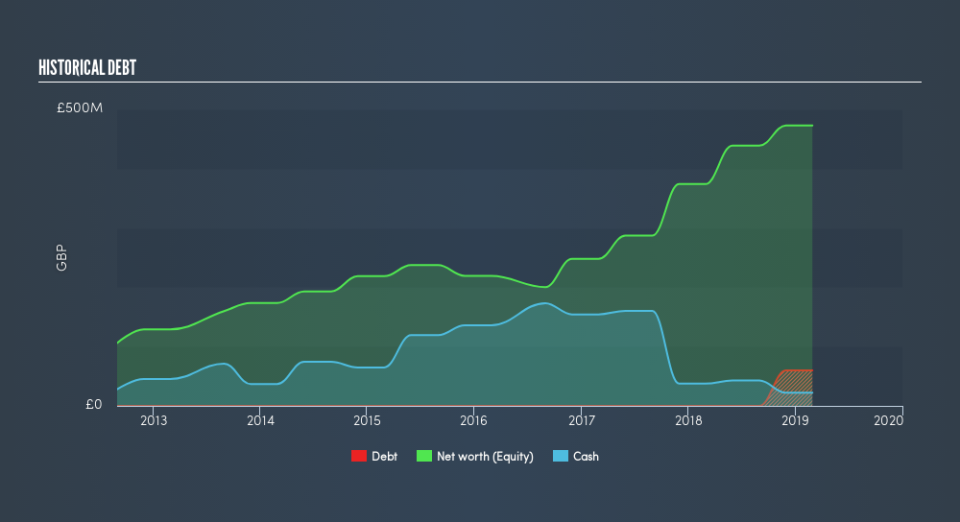
What Is ASOS's Net Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of February 2019, ASOS had UK£60.0m of debt, up from none a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, because it has a cash reserve of UK£22.1m, its net debt is less, at about UK£37.9m.
How Strong Is ASOS's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, ASOS had liabilities of UK£650.7m due within 12 months, and liabilities of UK£16.8m due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of UK£22.1m as well as receivables valued at UK£49.2m due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by UK£596.2m.
This deficit isn't so bad because ASOS is worth UK£2.15b, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
ASOS's net debt is only 0.37 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 128 times the size. So we're pretty relaxed about its super-conservative use of debt. On the other hand, ASOS saw its EBIT drop by 6.7% in the last twelve months. If earnings continue to decline at that rate the company may have increasing difficulty managing its debt load. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if ASOS can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last three years, ASOS burned a lot of cash. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
Neither ASOS's ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow nor its EBIT growth rate gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But the good news is it seems to be able to cover its interest expense with its EBIT with ease. When we consider all the factors discussed, it seems to us that ASOS is taking some risks with its use of debt. So while that leverage does boost returns on equity, we wouldn't really want to see it increase from here. In light of our reservations about the company's balance sheet, it seems sensible to check if insiders have been selling shares recently.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance