Should B&M European Value Retail S.A. (LON:BME) Focus On Improving This Fundamental Metric?

One of the best investments we can make is in our own knowledge and skill set. With that in mind, this article will work through how we can use Return On Equity (ROE) to better understand a business. By way of learning-by-doing, we'll look at ROE to gain a better understanding of B&M European Value Retail S.A. (LON:BME).
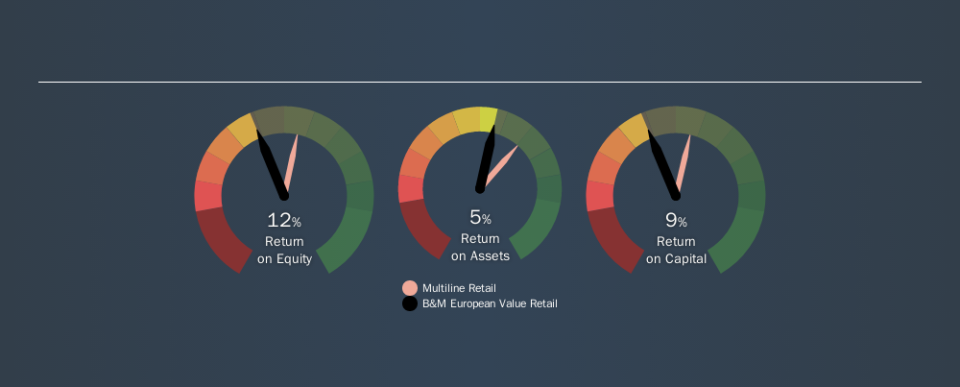
Over the last twelve months B&M European Value Retail has recorded a ROE of 12%. One way to conceptualize this, is that for each £1 of shareholders' equity it has, the company made £0.12 in profit.
See our latest analysis for B&M European Value Retail
How Do I Calculate Return On Equity?
The formula for ROE is:
Return on Equity = Net Profit ÷ Shareholders' Equity
Or for B&M European Value Retail:
12% = UK£132m ÷ UK£973m (Based on the trailing twelve months to September 2019.)
Most know that net profit is the total earnings after all expenses, but the concept of shareholders' equity is a little more complicated. It is all earnings retained by the company, plus any capital paid in by shareholders. The easiest way to calculate shareholders' equity is to subtract the company's total liabilities from the total assets.
What Does Return On Equity Signify?
ROE looks at the amount a company earns relative to the money it has kept within the business. The 'return' is the yearly profit. The higher the ROE, the more profit the company is making. So, all else equal, investors should like a high ROE. That means it can be interesting to compare the ROE of different companies.
Does B&M European Value Retail Have A Good Return On Equity?
Arguably the easiest way to assess company's ROE is to compare it with the average in its industry. The limitation of this approach is that some companies are quite different from others, even within the same industry classification. If you look at the image below, you can see B&M European Value Retail has a lower ROE than the average (18%) in the Multiline Retail industry classification.
Unfortunately, that's sub-optimal. We prefer it when the ROE of a company is above the industry average, but it's not the be-all and end-all if it is lower. Nonetheless, it could be useful to double-check if insiders have sold shares recently.
The Importance Of Debt To Return On Equity
Most companies need money -- from somewhere -- to grow their profits. That cash can come from retained earnings, issuing new shares (equity), or debt. In the first two cases, the ROE will capture this use of capital to grow. In the latter case, the debt used for growth will improve returns, but won't affect the total equity. Thus the use of debt can improve ROE, albeit along with extra risk in the case of stormy weather, metaphorically speaking.
Combining B&M European Value Retail's Debt And Its 12% Return On Equity
Although B&M European Value Retail does use debt, its debt to equity ratio of 0.80 is still low. The fact that it achieved a fairly good ROE with only modest debt suggests the business might be worth putting on your watchlist. Conservative use of debt to boost returns is usually a good move for shareholders, though it does leave the company more exposed to interest rate rises.
The Bottom Line On ROE
Return on equity is one way we can compare the business quality of different companies. In my book the highest quality companies have high return on equity, despite low debt. If two companies have the same ROE, then I would generally prefer the one with less debt.
But when a business is high quality, the market often bids it up to a price that reflects this. Profit growth rates, versus the expectations reflected in the price of the stock, are a particularly important to consider. So you might want to check this FREE visualization of analyst forecasts for the company.
If you would prefer check out another company -- one with potentially superior financials -- then do not miss thisfree list of interesting companies, that have HIGH return on equity and low debt.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance