Bayer (ETR:BAYN) Takes On Some Risk With Its Use Of Debt

Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital. When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Bayer Aktiengesellschaft (ETR:BAYN) does use debt in its business. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Bayer
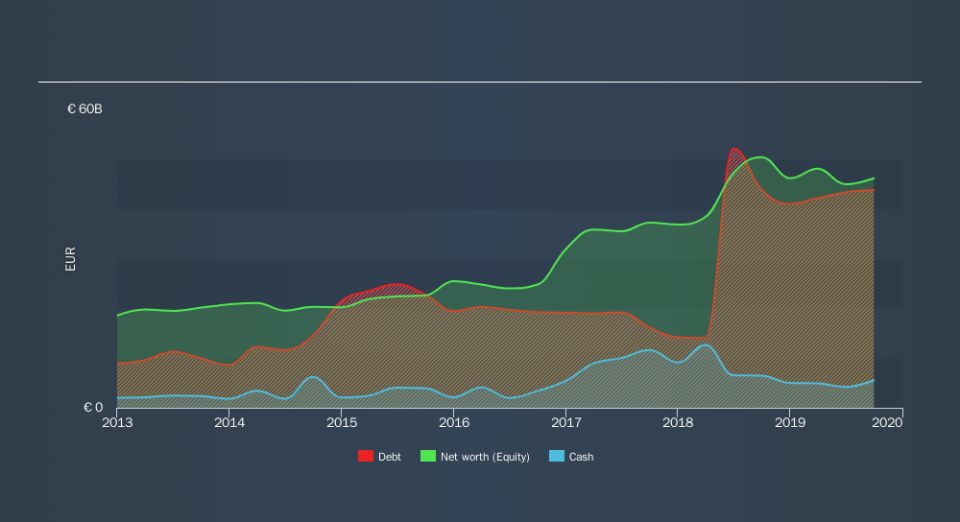
What Is Bayer's Net Debt?
As you can see below, Bayer had €43.4b of debt, at September 2019, which is about the same the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. However, it does have €5.55b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about €37.8b.
A Look At Bayer's Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, Bayer had liabilities of €26.1b due within 12 months, and liabilities of €58.6b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of €5.55b and €14.2b worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling €64.9b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This is a mountain of leverage even relative to its gargantuan market capitalization of €65.7b. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Weak interest cover of 0.36 times and a disturbingly high net debt to EBITDA ratio of 7.9 hit our confidence in Bayer like a one-two punch to the gut. The debt burden here is substantial. Even worse, Bayer saw its EBIT tank 94% over the last 12 months. If earnings keep going like that over the long term, it has a snowball's chance in hell of paying off that debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Bayer's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, Bayer actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. That sort of strong cash generation warms our hearts like a puppy in a bumblebee suit.
Our View
To be frank both Bayer's interest cover and its track record of (not) growing its EBIT make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at converting EBIT to free cash flow; that's encouraging. We're quite clear that we consider Bayer to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. For this reason we're pretty cautious about the stock, and we think shareholders should keep a close eye on its liquidity. Even though Bayer lost money on the bottom line, its positive EBIT suggests the business itself has potential. So you might want to check outhow earnings have been trending over the last few years.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance