Dewhurst plc's (LON:DWHT) Has Performed Well But Fundamentals Look Varied: Is There A Clear Direction For The Stock?

Most readers would already know that Dewhurst's (LON:DWHT) stock increased by 7.0% over the past three months. However, we decided to study the company's mixed-bag of fundamentals to assess what this could mean for future share prices, as stock prices tend to be aligned with a company's long-term financial performance. Particularly, we will be paying attention to Dewhurst's ROE today.
ROE or return on equity is a useful tool to assess how effectively a company can generate returns on the investment it received from its shareholders. In other words, it is a profitability ratio which measures the rate of return on the capital provided by the company's shareholders.
View our latest analysis for Dewhurst
How Is ROE Calculated?
Return on equity can be calculated by using the formula:
Return on Equity = Net Profit (from continuing operations) ÷ Shareholders' Equity
So, based on the above formula, the ROE for Dewhurst is:
7.5% = UK£3.1m ÷ UK£42m (Based on the trailing twelve months to March 2020).
The 'return' refers to a company's earnings over the last year. Another way to think of that is that for every £1 worth of equity, the company was able to earn £0.08 in profit.
What Is The Relationship Between ROE And Earnings Growth?
We have already established that ROE serves as an efficient profit-generating gauge for a company's future earnings. We now need to evaluate how much profit the company reinvests or "retains" for future growth which then gives us an idea about the growth potential of the company. Assuming everything else remains unchanged, the higher the ROE and profit retention, the higher the growth rate of a company compared to companies that don't necessarily bear these characteristics.
A Side By Side comparison of Dewhurst's Earnings Growth And 7.5% ROE
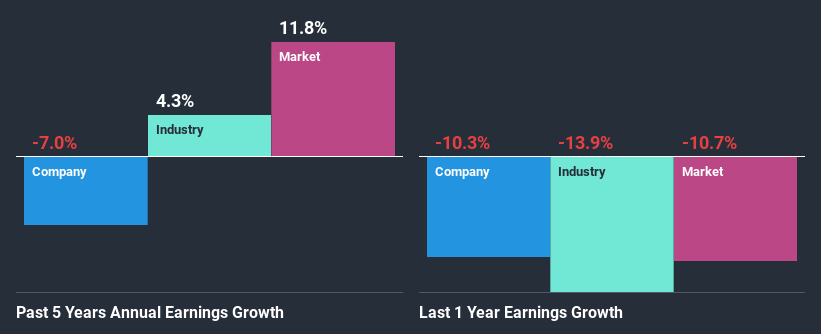
When you first look at it, Dewhurst's ROE doesn't look that attractive. Next, when compared to the average industry ROE of 11%, the company's ROE leaves us feeling even less enthusiastic. For this reason, Dewhurst's five year net income decline of 7.0% is not surprising given its lower ROE. We reckon that there could also be other factors at play here. For example, it is possible that the business has allocated capital poorly or that the company has a very high payout ratio.
That being said, we compared Dewhurst's performance with the industry and were concerned when we found that while the company has shrunk its earnings, the industry has grown its earnings at a rate of 4.3% in the same period.
Earnings growth is an important metric to consider when valuing a stock. It’s important for an investor to know whether the market has priced in the company's expected earnings growth (or decline). Doing so will help them establish if the stock's future looks promising or ominous. If you're wondering about Dewhurst's's valuation, check out this gauge of its price-to-earnings ratio, as compared to its industry.
Is Dewhurst Making Efficient Use Of Its Profits?
Despite having a normal three-year median payout ratio of 28% (where it is retaining 72% of its profits), Dewhurst has seen a decline in earnings as we saw above. So there could be some other explanations in that regard. For instance, the company's business may be deteriorating.
Moreover, Dewhurst has been paying dividends for at least ten years or more suggesting that management must have perceived that the shareholders prefer dividends over earnings growth.
Conclusion
Overall, we have mixed feelings about Dewhurst. While the company does have a high rate of profit retention, its low rate of return is probably hampering its earnings growth. Wrapping up, we would proceed with caution with this company and one way of doing that would be to look at the risk profile of the business. You can see the 2 risks we have identified for Dewhurst by visiting our risks dashboard for free on our platform here.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance