Does This Valuation Of Repsol, S.A. (BME:REP) Imply Investors Are Overpaying?

Does the January share price for Repsol, S.A. (BME:REP) reflect what it's really worth? Today, we will estimate the stock's intrinsic value by taking the expected future cash flows and discounting them to today's value. I will use the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model. Don't get put off by the jargon, the math behind it is actually quite straightforward.
Companies can be valued in a lot of ways, so we would point out that a DCF is not perfect for every situation. If you want to learn more about discounted cash flow, the rationale behind this calculation can be read in detail in the Simply Wall St analysis model.
View our latest analysis for Repsol
Step by step through the calculation
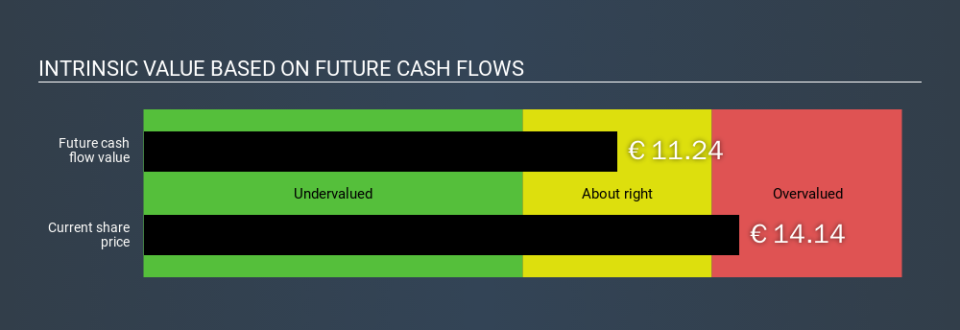
We have to calculate the value of Repsol slightly differently to other stocks because it is a oil and gas company. Instead of using free cash flows, which are hard to estimate and often not reported by analysts in this industry, dividends per share (DPS) payments are used. This often underestimates the value of a stock, but it can still be good as a comparison to competitors. The 'Gordon Growth Model' is used, which simply assumes that dividend payments will continue to increase at a sustainable growth rate forever. The dividend is expected to growth at an annual growth rate equal to the 10-year government bond rate of 0.4%. We then discount this figure to today's value at a cost of equity of 9.5%. Compared to the current share price of €14.1, the company appears slightly overvalued at the time of writing. The assumptions in any calculation have a big impact on the valuation, so it is better to view this as a rough estimate, not precise down to the last cent.
Value Per Share = Expected Dividend Per Share / (Discount Rate - Perpetual Growth Rate)
= €1.0 / (9.5% – 0.4%)
= €11.2
Important assumptions
The calculation above is very dependent on two assumptions. The first is the discount rate and the other is the cash flows. Part of investing is coming up with your own evaluation of a company's future performance, so try the calculation yourself and check your own assumptions. The DCF also does not consider the possible cyclicality of an industry, or a company's future capital requirements, so it does not give a full picture of a company's potential performance. Given that we are looking at Repsol as potential shareholders, the cost of equity is used as the discount rate, rather than the cost of capital (or weighted average cost of capital, WACC) which accounts for debt. In this calculation we've used 9.5%, which is based on a levered beta of 1.225. Beta is a measure of a stock's volatility, compared to the market as a whole. We get our beta from the industry average beta of globally comparable companies, with an imposed limit between 0.8 and 2.0, which is a reasonable range for a stable business.
Next Steps:
Valuation is only one side of the coin in terms of building your investment thesis, and it shouldn’t be the only metric you look at when researching a company. The DCF model is not a perfect stock valuation tool. Rather it should be seen as a guide to "what assumptions need to be true for this stock to be under/overvalued?" If a company grows at a different rate, or if its cost of equity or risk free rate changes sharply, the output can look very different. What is the reason for the share price to differ from the intrinsic value? For Repsol, I've put together three essential aspects you should look at:
Financial Health: Does REP have a healthy balance sheet? Take a look at our free balance sheet analysis with six simple checks on key factors like leverage and risk.
Future Earnings: How does REP's growth rate compare to its peers and the wider market? Dig deeper into the analyst consensus number for the upcoming years by interacting with our free analyst growth expectation chart.
Other High Quality Alternatives: Are there other high quality stocks you could be holding instead of REP? Explore our interactive list of high quality stocks to get an idea of what else is out there you may be missing!
PS. Simply Wall St updates its DCF calculation for every ES stock every day, so if you want to find the intrinsic value of any other stock just search here.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance