Glaxo to make a billion doses of Covid vaccine booster
GlaxoSmithKline is ramping up production of its vaccine booster to manufacture 1bn doses that could be used to help with coronavirus immunisation as early as next year.
The FTSE 100 pharmaceuticals firm - one of the world’s biggest vaccine manufacturers - said its immunisation booster, or “adjuvant”, has the potential to improve how effective Covid-19 vaccines are as scientists aronud the world race to beat the disease.
Adjuvants can reduce the amount of a virus needed to produce a vaccine, allowing more doses to be made and helping to protect more people.
They are also used in some vaccines to boost the immune response of a patient, which can enable a stronger and longer-lasting immunity against infections.
Adam Barker, a healthcare analyst at Shore Capital, said: "At a minimum, the need for smaller amounts of virus material per vaccine means that more vaccine can be produced in a quicker time period."
GSK said it has started to manufacture the adjuvant “at risk”, meaning there is no certainty the extra volumes produced will be needed.
Meanwhile, cell and gene firm Oxford Biomedica said it has struck a deal with drug titan AstraZeneca to manufacture an experimental Covid-19 vaccine which is seen as one of the global frontrunners in the race for immunity.
Oxford BioMedica will provide AstraZeneca with multiple batches of the vaccine, called AZD1222, under a one-year clinical and commercial supply agreement. The company expects most doses to be produced this year.
AstraZeneca is also lending its manufacturing and distributing capabilities to the University of Oxford, which it hopes will enable the delivery of up to 100m doses by Christmas.
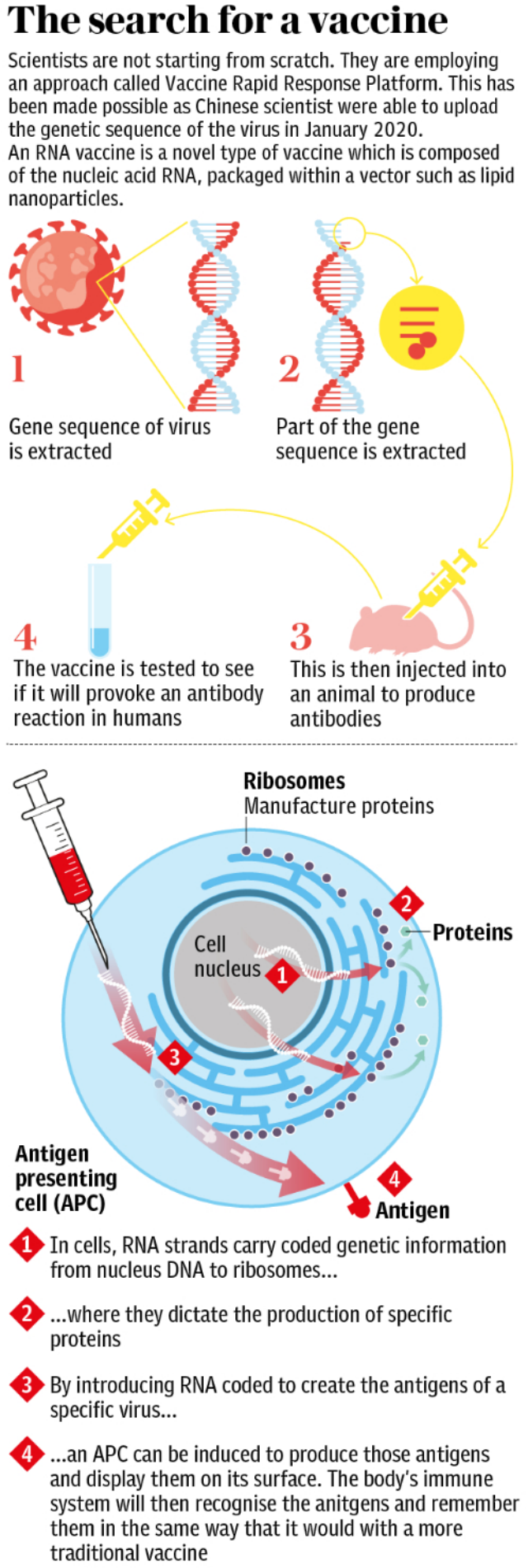
Glaxo has already joined forces with French rival Sanofi to provide its adjuvant technology for the development of a protein-based vaccine, which will see Sanofi provide its S-protein Covid-19 antigen to create an immune response to the vaccine.
The company is also in discussions with governments and global institutions about funding for production and supply of the adjuvant.
Bosses said Glaxo does not expect to profit from any of its contributions to the development of a vaccine for coronavirus. It will invest any income into coronavirus-related research and long-term pandemic preparedness.
The pharmaceuticals firm said it plans to make the adjuvant available to countries that cannot necessarily afford it by working with governments and global institutions.
Emma Walmsley, chief executive of Glaxo, has warned previously that more than one vaccine will be needed to overcome the pandemic due to the scale of demand across the world.
Mr Barker said different vaccines are likely to promote different immune responses, meaning multiple vaccines will be necessary, particularly if the virus changes. Some vaccines may not be suitable for certain patients, he said, further increasing the need for alternatives.
Roger Connor, global vaccines president at Glaxo, said: “We believe that our innovative pandemic adjuvant technology has the potential to help improve the efficacy and scale up of multiple Covid-19 vaccines.
"With this significant expansion in our manufacturing capacity, we can help deliver up to 1bn doses of adjuvanted vaccines through 2021, helping protect many more people and support the global effort to fight Covid-19.”

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 