'Grexit' is back

Jim Edwards
Greeks are pulling billions out of their banks in fear of new cash controls.
Greece's economy is shrinking again.
The country has not been able to put together a deal to pay off its next debt payment.
People are talking seriously about "Grexit" again.
Greece's banks lost about €4 billion in bank deposits since the turn of the year as Greeks fear a return of capital controls that ban them from making cash withdrawals over set limits. Separately, the country looks as if it is tipping back into recession — GDP shrank by 1.2% in Q4 2016.
Does this story sound familiar?
It should. A collapsing economy followed by a run on the banks were the signal events of the Greek debt crisis that began in 2009 and never really ended.
So now people are asking — again — whether Greece might be forced out of the eurozone:
Germany's Bavarian finance minister, Markus Soeder, said this week that “Greece is unlikely to survive in the eurozone over the long term.”
German opposition politician Christian Lindner said that Greece should abandon the euro and be offered debt relief.
And Pantheon Macroeconomics analyst Claus Vistesen wrote in a recent note to clients:
"Assets held by a benchmark Athens-based money market fund are down 11% in the past six months. This suggests that investors are beginning to price in the risk of a Greek exit from the Eurozone."
"... Households’ overnight deposits fell 1.1% year-over-year in January, indicating that liquidity in the private sector is drying up. Amazingly, Greece and its creditors are sleepwalking toward a repeat of the chaos in 2015, when capital controls were enforced to prevent a collapse of the banks."
Today, the ECB added another €400 million in emergency liquidity assistance to the Greek central bank, a move that "reflects developments in the liquidity situation of Greek banks, taking into account private sector deposit flows,” the ECB said.
This is what the Greek bank run looks like so far, per Pantheon:
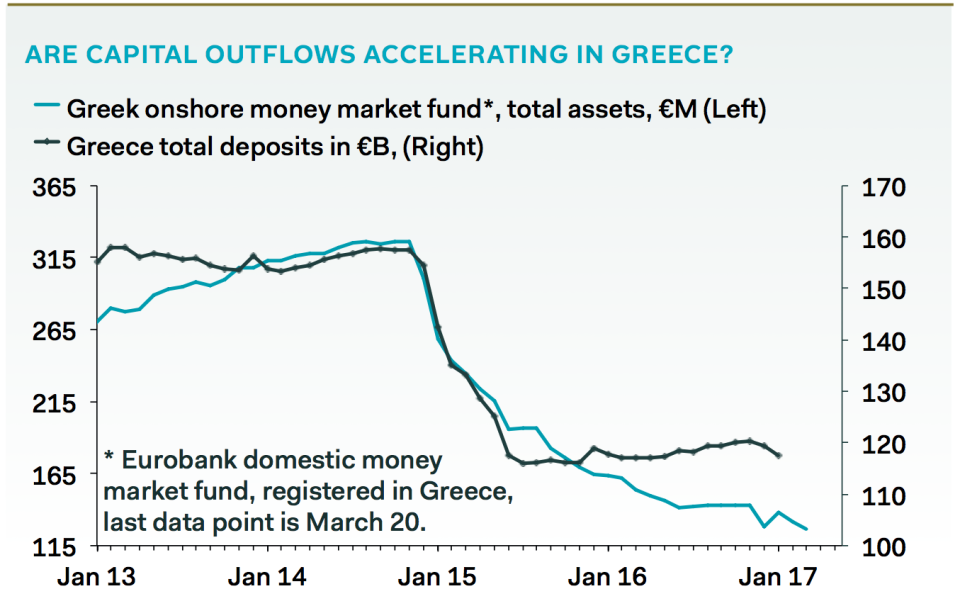
Pantheon Economics The economy, which has been through worse than the Great Depression in the U.S., has started to falter again after showing signs of recovery:
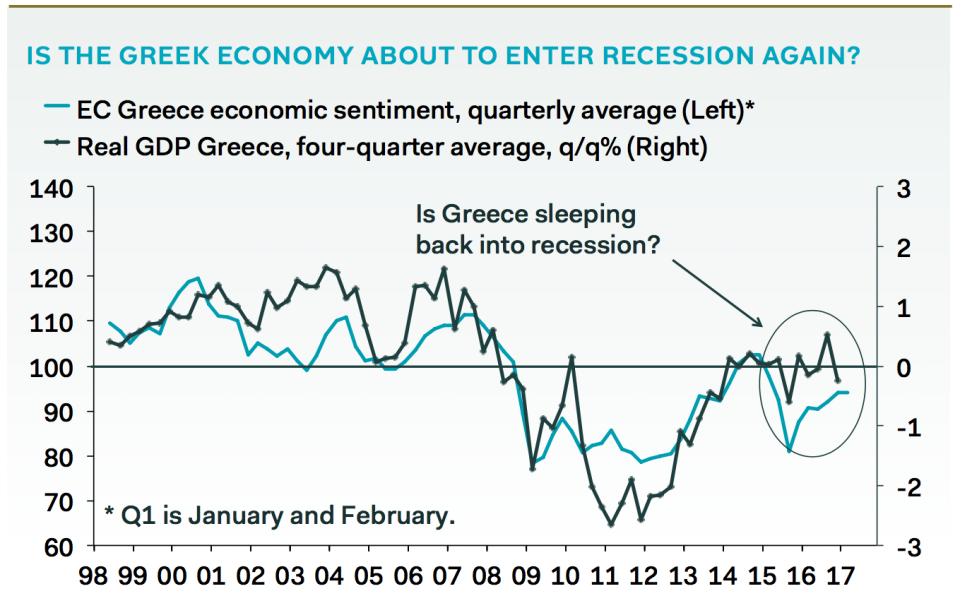
Pantheon Economics
A debt payment of €7 billion is due in July and the Greek government has not yet managed to reach a deal with the ECB and the IMF. "Greece’s current position in the Eurozone is untenable; something has to give," says Vistesen.
Although Alexis Tsipras's Syriza-led government has made some economic reforms and privatised some industries, Tsipras has not budged on cuts to Greek pensions, which are 13.3% of Greece's GDP — far more than other countries, Pantheon says. (For comparison, UK pension spending per GDP is roughly half that, according to the IFS.)
The intractable aspect of Greece is that its economy is too small to handle the amount of debt it is being asked to pay.
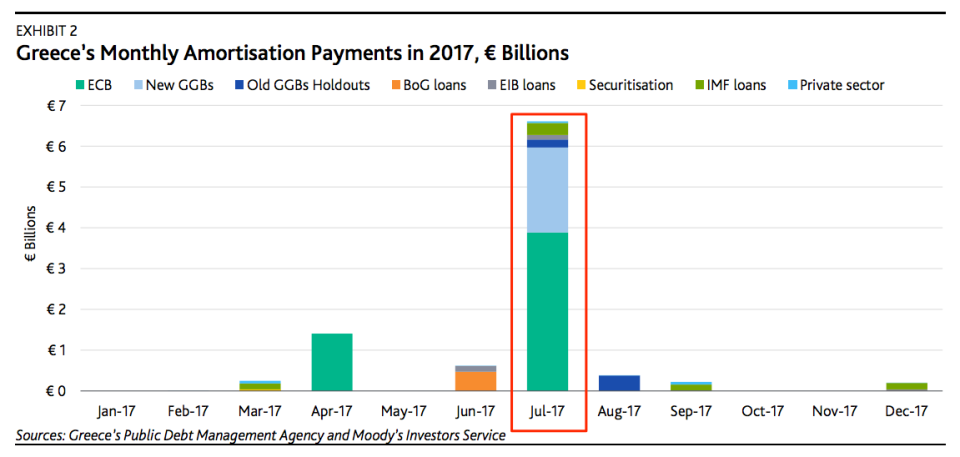
Moody's
Note that most of the payment due in July is owed to the ECB and IMF. The IMF increasingly regards its role in Greece as a disaster. Internally, the debt is regarded as "unsustainable" according to a document leaked to the Wall Street Journal.
Even if Greece fully implemented all the reforms the IMF has demanded its economy would not become large enough to pay off the debt. Its debt load as a portion of GDP is going up, even as it makes payments. (The fact that Greek terrorists are now bombing local IMF targets probably isn't helping, either.)
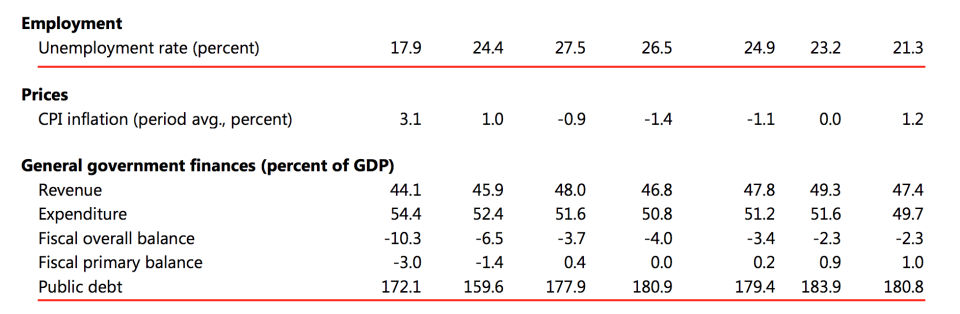
IMF
So now Greece has all the disadvantages of monetary union and none of the advantages. It owes money to Europe, but cannot receive investment from Europe. Vistesen again:
The economy is saddled with fiscal controls from the EU, but it receives none of the benefits of monetary union. The ECB has boosted its balance sheet by 80% since 2015, but has been unable to buy Greek bonds and Greek banks have not had full access to the central bank’s liquidity provisions.
Bizarrely, US President Trump may help make the case for debt relief. He reportedly intends to nominate Adam Lerrick — an IMF critic — as the Under-Secretary of the Treasury for international finance.
That will give the IMF more negative optics to deal with, and a greater temptation to announce that it is writing off more of the debt. Or Greece could just default out of the eurozone.
Stranger things have happened: Before the term "Brexit" was invented, "Grexit" was the far better-known word — and the more plausible scenario.
NOW WATCH: A $2.5 trillion asset manager just put a statue of a defiant girl in front of the Wall Street bull
See Also:
SEE ALSO: Greece is in trouble again over its 'explosive' debt — here's why
AND: MONTI: A good Article 50 deal for the UK would mean 'organised suicide' for the EU
DON'T MISS: The ECB admits people in Europe are getting poorer

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 
