Here's Why Intel (NASDAQ:INTC) Can Manage Its Debt Responsibly

Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We note that Intel Corporation (NASDAQ:INTC) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Intel
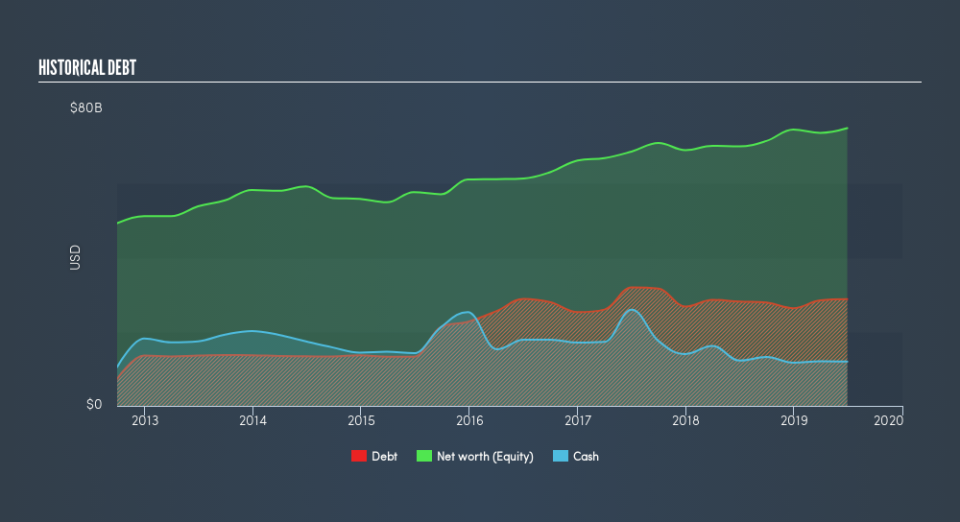
How Much Debt Does Intel Carry?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Intel had US$28.8b in debt in June 2019; about the same as the year before. However, because it has a cash reserve of US$11.9b, its net debt is less, at about US$16.9b.
How Healthy Is Intel's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Intel had liabilities of US$19.7b due within 12 months and liabilities of US$36.1b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$11.9b as well as receivables valued at US$6.29b due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$37.6b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Given Intel has a humongous market capitalization of US$205.4b, it's hard to believe these liabilities pose much threat. However, we do think it is worth keeping an eye on its balance sheet strength, as it may change over time.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Intel has a low net debt to EBITDA ratio of only 0.52. And its EBIT covers its interest expense a whopping 4k times over. So you could argue it is no more threatened by its debt than an elephant is by a mouse. Fortunately, Intel grew its EBIT by 9.9% in the last year, making that debt load look even more manageable. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Intel can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the most recent three years, Intel recorded free cash flow worth 64% of its EBIT, which is around normal, given free cash flow excludes interest and tax. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
Our View
Intel's interest cover suggests it can handle its debt as easily as Cristiano Ronaldo could score a goal against an under 14's goalkeeper. And that's just the beginning of the good news since its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow is also very heartening. Taking all this data into account, it seems to us that Intel takes a pretty sensible approach to debt. While that brings some risk, it can also enhance returns for shareholders. Of course, we wouldn't say no to the extra confidence that we'd gain if we knew that Intel insiders have been buying shares: if you're on the same wavelength, you can find out if insiders are buying by clicking this link.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance