Institutional owners may take dramatic actions as Virgin Money UK PLC's (LON:VMUK) recent 3.9% drop adds to one-year losses
Key Insights
Significantly high institutional ownership implies Virgin Money UK's stock price is sensitive to their trading actions
The top 10 shareholders own 51% of the company
Ownership research along with analyst forecasts data help provide a good understanding of opportunities in a stock
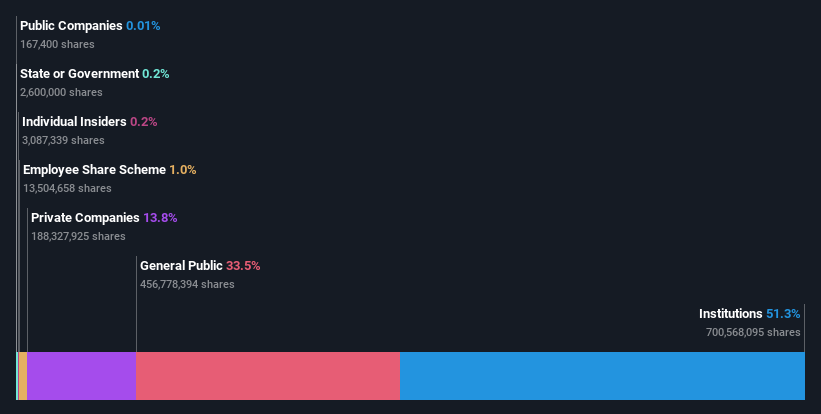
Every investor in Virgin Money UK PLC (LON:VMUK) should be aware of the most powerful shareholder groups. We can see that institutions own the lion's share in the company with 51% ownership. Put another way, the group faces the maximum upside potential (or downside risk).
As a result, institutional investors endured the highest losses last week after market cap fell by UK£82m. Needless to say, the recent loss which further adds to the one-year loss to shareholders of 14% might not go down well especially with this category of shareholders. Institutions or "liquidity providers" control large sums of money and therefore, these types of investors usually have a lot of influence over stock price movements. As a result, if the downtrend continues, institutions may face pressures to sell Virgin Money UK, which might have negative implications on individual investors.
Let's take a closer look to see what the different types of shareholders can tell us about Virgin Money UK.
View our latest analysis for Virgin Money UK
What Does The Institutional Ownership Tell Us About Virgin Money UK?
Institutional investors commonly compare their own returns to the returns of a commonly followed index. So they generally do consider buying larger companies that are included in the relevant benchmark index.
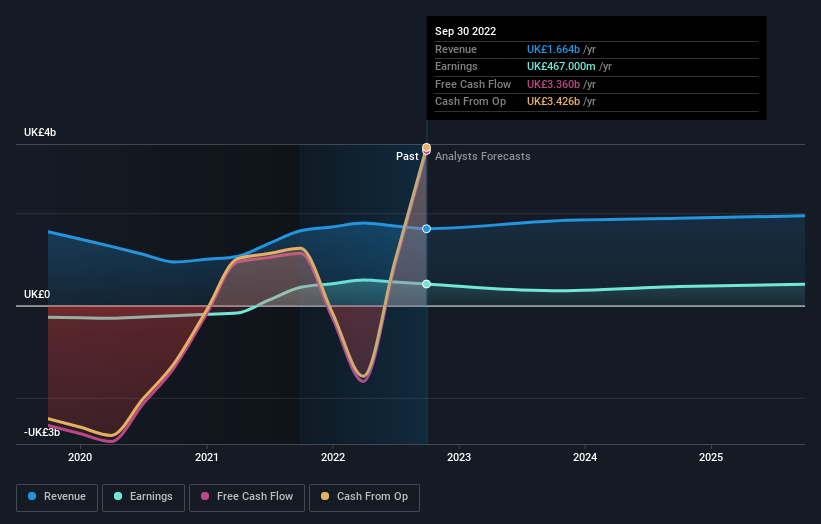
We can see that Virgin Money UK does have institutional investors; and they hold a good portion of the company's stock. This implies the analysts working for those institutions have looked at the stock and they like it. But just like anyone else, they could be wrong. When multiple institutions own a stock, there's always a risk that they are in a 'crowded trade'. When such a trade goes wrong, multiple parties may compete to sell stock fast. This risk is higher in a company without a history of growth. You can see Virgin Money UK's historic earnings and revenue below, but keep in mind there's always more to the story.
Since institutional investors own more than half the issued stock, the board will likely have to pay attention to their preferences. Virgin Money UK is not owned by hedge funds. Looking at our data, we can see that the largest shareholder is Virgin Group Holdings Limited with 14% of shares outstanding. In comparison, the second and third largest shareholders hold about 11% and 5.3% of the stock.
We also observed that the top 10 shareholders account for more than half of the share register, with a few smaller shareholders to balance the interests of the larger ones to a certain extent.
Researching institutional ownership is a good way to gauge and filter a stock's expected performance. The same can be achieved by studying analyst sentiments. There are a reasonable number of analysts covering the stock, so it might be useful to find out their aggregate view on the future.
Insider Ownership Of Virgin Money UK
While the precise definition of an insider can be subjective, almost everyone considers board members to be insiders. The company management answer to the board and the latter should represent the interests of shareholders. Notably, sometimes top-level managers are on the board themselves.
Insider ownership is positive when it signals leadership are thinking like the true owners of the company. However, high insider ownership can also give immense power to a small group within the company. This can be negative in some circumstances.
Our information suggests that Virgin Money UK PLC insiders own under 1% of the company. However, it's possible that insiders might have an indirect interest through a more complex structure. Keep in mind that it's a big company, and the insiders own UK£4.5m worth of shares. The absolute value might be more important than the proportional share. It is good to see board members owning shares, but it might be worth checking if those insiders have been buying.
General Public Ownership
The general public, who are usually individual investors, hold a 33% stake in Virgin Money UK. While this size of ownership may not be enough to sway a policy decision in their favour, they can still make a collective impact on company policies.
Private Company Ownership
We can see that Private Companies own 14%, of the shares on issue. It might be worth looking deeper into this. If related parties, such as insiders, have an interest in one of these private companies, that should be disclosed in the annual report. Private companies may also have a strategic interest in the company.
Next Steps:
I find it very interesting to look at who exactly owns a company. But to truly gain insight, we need to consider other information, too. Consider for instance, the ever-present spectre of investment risk. We've identified 3 warning signs with Virgin Money UK (at least 1 which is potentially serious) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
Ultimately the future is most important. You can access this free report on analyst forecasts for the company.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Join A Paid User Research Session
You’ll receive a US$30 Amazon Gift card for 1 hour of your time while helping us build better investing tools for the individual investors like yourself. Sign up here

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance