Are Intel Corporation's (NASDAQ:INTC) Mixed Financials Driving The Negative Sentiment?
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC) has had a rough three months with its share price down 21%. We, however decided to study the company's financials to determine if they have got anything to do with the price decline. Stock prices are usually driven by a company’s financial performance over the long term, and therefore we decided to pay more attention to the company's financial performance. Particularly, we will be paying attention to Intel's ROE today.
ROE or return on equity is a useful tool to assess how effectively a company can generate returns on the investment it received from its shareholders. In short, ROE shows the profit each dollar generates with respect to its shareholder investments.
See our latest analysis for Intel
How To Calculate Return On Equity?
The formula for return on equity is:
Return on Equity = Net Profit (from continuing operations) ÷ Shareholders' Equity
So, based on the above formula, the ROE for Intel is:
1.5% = US$1.7b ÷ US$110b (Based on the trailing twelve months to December 2023).
The 'return' is the profit over the last twelve months. One way to conceptualize this is that for each $1 of shareholders' capital it has, the company made $0.02 in profit.
Why Is ROE Important For Earnings Growth?
So far, we've learned that ROE is a measure of a company's profitability. We now need to evaluate how much profit the company reinvests or "retains" for future growth which then gives us an idea about the growth potential of the company. Assuming everything else remains unchanged, the higher the ROE and profit retention, the higher the growth rate of a company compared to companies that don't necessarily bear these characteristics.
Intel's Earnings Growth And 1.5% ROE
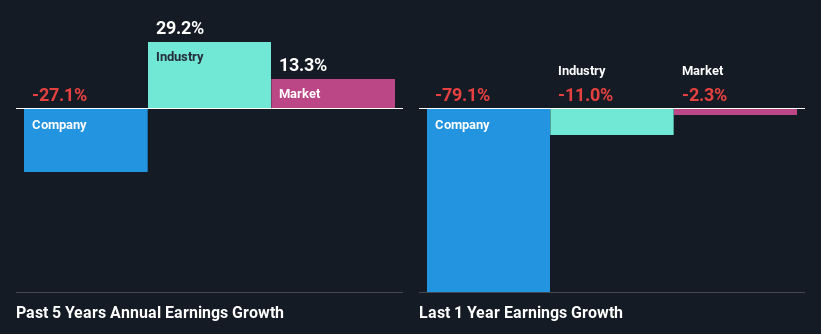
It is hard to argue that Intel's ROE is much good in and of itself. Not just that, even compared to the industry average of 14%, the company's ROE is entirely unremarkable. For this reason, Intel's five year net income decline of 27% is not surprising given its lower ROE. We believe that there also might be other aspects that are negatively influencing the company's earnings prospects. For example, the business has allocated capital poorly, or that the company has a very high payout ratio.
So, as a next step, we compared Intel's performance against the industry and were disappointed to discover that while the company has been shrinking its earnings, the industry has been growing its earnings at a rate of 29% over the last few years.
Earnings growth is an important metric to consider when valuing a stock. The investor should try to establish if the expected growth or decline in earnings, whichever the case may be, is priced in. By doing so, they will have an idea if the stock is headed into clear blue waters or if swampy waters await. Is Intel fairly valued compared to other companies? These 3 valuation measures might help you decide.
Is Intel Efficiently Re-investing Its Profits?
In spite of a normal three-year median payout ratio of 29% (that is, a retention ratio of 71%), the fact that Intel's earnings have shrunk is quite puzzling. It looks like there might be some other reasons to explain the lack in that respect. For example, the business could be in decline.
Additionally, Intel has paid dividends over a period of at least ten years, which means that the company's management is determined to pay dividends even if it means little to no earnings growth. Existing analyst estimates suggest that the company's future payout ratio is expected to drop to 18% over the next three years. The fact that the company's ROE is expected to rise to 8.6% over the same period is explained by the drop in the payout ratio.
Summary
Overall, we have mixed feelings about Intel. Even though it appears to be retaining most of its profits, given the low ROE, investors may not be benefitting from all that reinvestment after all. The low earnings growth suggests our theory correct. With that said, we studied the latest analyst forecasts and found that while the company has shrunk its earnings in the past, analysts expect its earnings to grow in the future. To know more about the company's future earnings growth forecasts take a look at this free report on analyst forecasts for the company to find out more.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance