Who Are The Largest Shareholders In Carrefour SA (EPA:CA)?

Today, I will be analyzing Carrefour SA’s (ENXTPA:CA) recent ownership structure, an important but not-so-popular subject among individual investors. Ownership structure has been found to have an impact on shareholder returns in both short- and long-term. Since the same amount of capital coming from an activist institution and a passive mutual fund has different implications on corporate governance, it is a useful exercise to deconstruct CA’s shareholder registry.
See our latest analysis for Carrefour
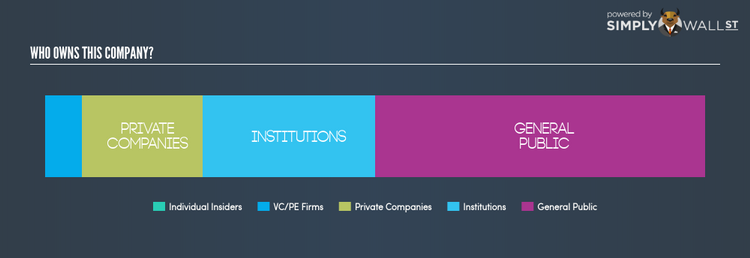
Institutional Ownership
With an institutional ownership of 26.21%, CA can face volatile stock price movements if institutions execute block trades on the open market, more so, when there are relatively small amounts of shares available on the market to trade However, as not all institutions are alike, such high volatility events, especially in the short-term, have been more frequently linked to active market participants like hedge funds. In the case of CA, investors need not worry about such volatility considering active hedge funds don’t have a significant stake. However, we should dig deeper into CA’s ownership structure and find out how other key ownership classes can affect its investment profile.
Insider Ownership
I find insiders are another important group of stakeholders, who are directly involved in making key decisions related to the use of capital. In essence, insider ownership is more about the alignment of shareholders’ interests with the management. CA insiders may only hold a a minor stake in the company, but this is a relatively significant holding given it is a large-cap stock. A higher level of insider ownership has been linked to management executing on high-returning projects instead of expansion projects for the sake of apparent growth. I will also like to check what insiders have been doing recently with their holdings. Insider buying may be a sign of upbeat future expectations, however, selling doesn’t necessarily mean the opposite as insiders may be motivated by their personal financial needs.
General Public Ownership
The general public holds a substantial 49.86% stake in CA, making it a highly popular stock among retail investors. With this size of ownership, retail investors can collectively play a role in major company policies that affect shareholders returns, including executive remuneration and the appointment of directors. They can also exercise the power to decline an acquisition or merger that may not improve profitability.
Private Equity Ownership
With a stake of 5.62%, private equity firms form another important class of owners in CA. With a stake of 5.62%, they can influence CA’s key policy decisions. This is a positive sign for potential investors as these firms play an important role in aligning company policy with shareholder returns.
Private Company Ownership
Potential investors in CA should also look at another important group of investors: private companies, with a stake of 18.23%, who are primarily invested because of strategic and capital gain interests. With this size of ownership in CA, this ownership class can affect the company’s business strategy. As a result, potential investors should further explore the company’s business relations with these companies and find out if they can affect shareholder returns in the long-term.
Next Steps:
The company’s high institutional ownership makes margin of safety a very important consideration to existing investors since long bull and bear trends often emerge when these big-ticket investors see a change in long-term potential of the company. This will allow investors to reduce the impact of non-fundamental factors, such as volatile block trading impact on their portfolio value. However, ownership structure should not be the only focus of your research when constructing an investment thesis around CA. Rather, you should be looking at fundamental drivers such as Carrefour’s past track record and financial health. I highly recommend you to complete your research by taking a look at the following:
Future Outlook: What are well-informed industry analysts predicting for CA’s future growth? Take a look at our free research report of analyst consensus for CA’s outlook.
Past Track Record: Has CA been consistently performing well irrespective of the ups and downs in the market? Go into more detail in the past performance analysis and take a look at the free visual representations of CA’s historicals for more clarity.
Other High-Performing Stocks: Are there other stocks that provide better prospects with proven track records? Explore our free list of these great stocks here.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
To help readers see pass the short term volatility of the financial market, we aim to bring you a long-term focused research analysis purely driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis does not factor in the latest price sensitive company announcements.
The author is an independent contributor and at the time of publication had no position in the stocks mentioned.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance