Why the eye-watering cost of Labour’s green pledge didn’t add up
As he took to the stage in Brighton to address members of the GMB, Sir Keir Starmer sought to tamp down a row over Labour’s green energy plans with promises of “good, union jobs”.
But what he left out of the speech on Tuesday was almost as revealing as what he put in.
There was no mention at all of what has been, until recently, Labour’s flagship pledge: a plan to borrow £28bn a year – for five years – and plough the money into green energy infrastructure.
Overall, the “Green Prosperity Plan” could have seen a Starmer government borrow a whopping £140bn if his party won power. It was designed to carpet the country with wind farms and solar panels that Sir Keir and his party believe will generate energy, jobs and growth.
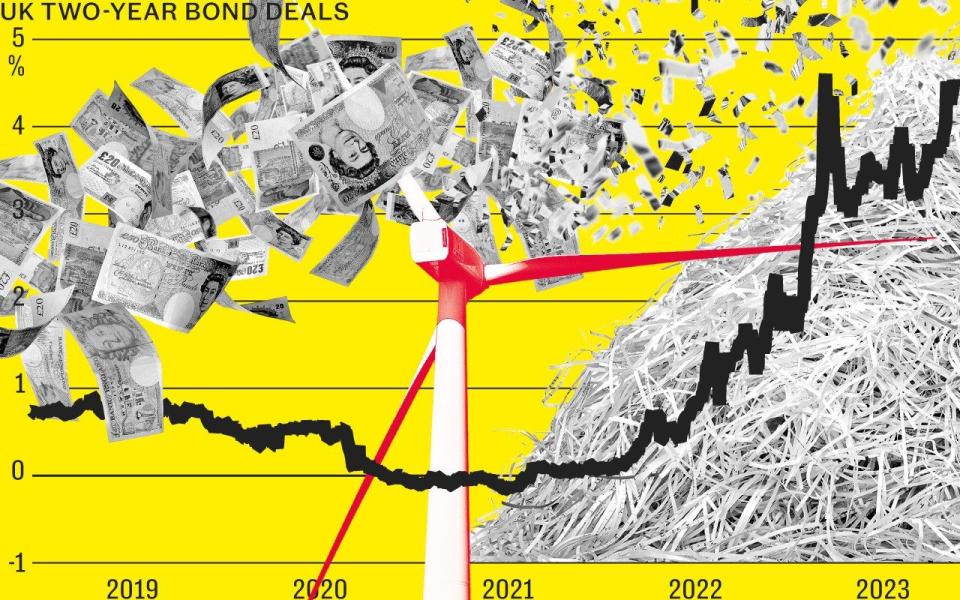
However, the borrowing spree threatened to pile more pressure on the country’s already stretched finances at a time when the market meltdown triggered by Liz Truss’s “mini-Budget” remains fresh in the collective memory.
On Friday, Labour’s plan was scrapped. Shadow chancellor Rachel Reeves blamed the about-turn on the Tories who she claimed had “crashed our economy”.
She told BBC Radio 4’s Today programme: “The other thing that has happened in last two years is the Tories have crashed our economy, and as a result interest rates have gone up 12 times, inflation is now at 8.7pc and I’ve always said that our fiscal rules are non-negotiable.
“Economic stability, financial stability, always has to come first and it will do with Labour. That’s why it’s important to ramp up and phase up our plans to get to the investment we need to secure these jobs so that it is also consistent with those fiscal rules to get debt down as a share of GDP and to balance day-to-day spending.”
Labour’s plan was dependent on the support and goodwill of strangers: To borrow this kind of money required, the Government will go to international markets, probably through the issuance of government bonds (also known as gilts).
In recent months, shadow cabinet members are said to have become increasingly nervous that borrowing such a large sum looks profligate against a backdrop of rising interest rates.
Complicating the picture is the fact that the Bank of England is embarking on a programme of bond selling after more than a decade of bond buying to prop up the economy. A more saturated market means bond investors will want fatter returns for their lending.
At the very least, say economists, this would have made it harder for Rachel Reeves, the shadow chancellor, to stick to her “fiscal rule” of reducing the national debt as a share of the economy without imposing spending cuts or tax rises.
At worst, some in the City fear Labour’s plan risked a debt crisis of the likes seen last September.
“The fiscal headroom that the Chancellor has been trying to maintain is around £30bn,” says Karl Williams, deputy research director at the Centre for Policy Studies (CPS).
“If you borrow £28bn, you are basically wiping out all of that. You have no wiggle room to stay within the fiscal targets that have been designed to try and reassure markets.
“That is therefore tax rise territory.”
Labour’s green energy spending plans were first announced by Reeves, to much fanfare, at the party’s annual conference almost two years ago.
They would involve borrowing tens of billions to invest in projects needed for Britain’s transition to clean power, including wind farm subsidies, home insulation, electric vehicle battery factories and a new generation of nuclear power stations, according to the Financial Times.
This would tie in with a policy to make the entire electricity grid “net zero” by 2030 – five years sooner than the Conservatives have promised – and a plan to set up Great British Energy, a publicly owned company that would invest and take stakes in energy schemes.
“We will provide certainty and show leadership in this decisive decade. I will be a responsible chancellor,” Reeves told party colleagues in 2021. “I will be Britain’s first green chancellor.”
The fiscal environment has changed dramatically since then.
Most notably, the Government is still doing penance for the fiscal policies of the short-lived Truss administration, which sent bond markets into meltdown. The “mini-Budget” that unveiled £45bn of unfunded tax cuts aimed at jump-starting the economy, yet in the event simply sent borrowing costs soaring.
One key question facing Labour is whether its own borrowing proposals will be viewed with more credibility. The answer depends on whether investors believe that the party’s spending spree will really put rocket boosters under the economy.
“There is a judgement on the efficacy of public sector spending,” says Simon French, managing director of Panmure Gordon.
In September, investors didn’t feel that the mini-Budget was “a good use of public resources”, he says, which triggered market scepticism and demands for higher yields.
James Alexander, chief executive of the UK Sustainable Investment and Finance Association, which represents fund giants including Abrdn, M&G, Aviva and Fidelity, argues that borrowing for investment in renewables is a different proposition.
“The Truss mini-Budget was a snap announcement of absolutely enormous amounts of borrowing and simultaneous tax cuts that no one had expected,” he explains.
“It took everyone by surprise and there was a very strong sense that it wasn’t costed, so there were many factors there that spooked the markets very, very quickly.”
In Labour’s case, many don’t think a UK government would have much trouble flogging £28bn of extra bonds to investors, particularly to pension funds.
“Pension funds have got millions and millions of pensioners who are all getting older,” says Steve Webb, a former pensions minister who is now a partner at advisory firm Lane Clark & Peacock.
“So underlying demand for bonds is going to go up, no matter who is in power. It is hard to believe a UK government could not shift a significant amount of bonds if it really wanted to.”
A more thorny issue for Labour may come in the form of interest rates. When Reeves committed to her borrowing plan, the Bank of England’s base rate stood at the record low of 0.1pc.
Today, it is 4.5pc and investors expect further rises will take it to a peak of 5.5pc.
At the same time, Threadneedle Street has switched from being a net buyer of bonds to a net seller, a process known as quantitative tightening.
This means there is more supply of gilts, so private sector buyers will demand higher yields.
The net effect of all this is higher borrowing costs for the UK Government on international markets, says CPS’s Williams.
Overall, Labour’s plan could have increased the national debt interest burden by £4.4bn a year, according to calculations by the Centre for Economics and Business Research.
Professor Jagjit Chadha, director of the National Institute of Economic and Social Research, says: “In an environment of sluggish economic growth, a large debt burden and rising gilt yields, a material increase in the debt issuance will be pretty hard for financial markets to swallow.
Even a successful raising of the debt carries risks. Public sector borrowing is already at a 60-year high, with the Office for Budget Responsibility expecting spending on debt interest relative to GDP to soon reach the highest level on record.
Taking on even more debt will make it harder for a future Chancellor to get debt falling again. Reeves has said she is committed to bringing down the national debt as a share of the economy.
Britain has a debt-to-GDP ratio close to 100pc and is close to falling into a “debt trap”, warns Gerard Lyons, chief economist strategist at Netwealth, where growth is too weak. This is similar to “maxing out on your credit card and not being able to afford the monthly interest rate payments”.
If there is not enough economic growth, the Government will need to balance the books by slashing spending or raising taxes.
Starmer and Reeves therefore must walk a narrow path if they are to persuade financial markets that their plans are as robust as they say.
“Has the scale of the landscape changed? Yes,” says French.
“Has the hurdle rate increased? Yes. All of those things are arithmetically true and nobody in the Labour Party should deny it.”

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 