Borrowing soars as runaway inflation pushes up interest
Interest payments on the UK’s debt helped push up borrowing last month, new official data shows.
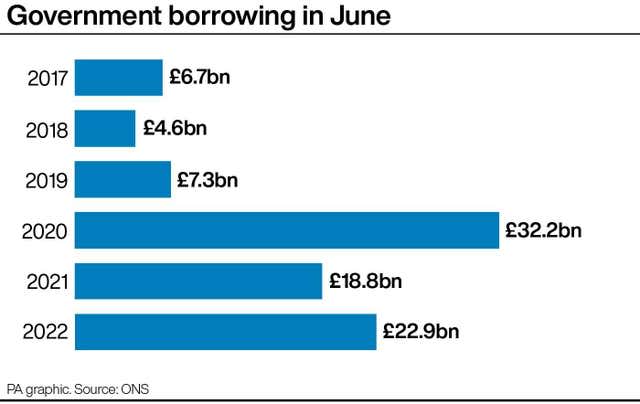
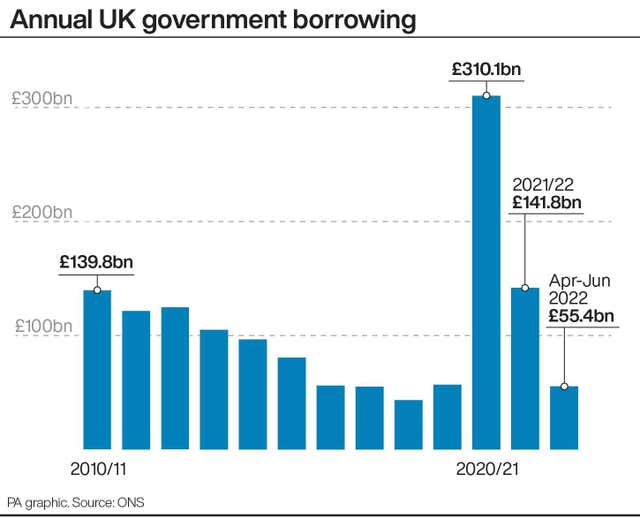
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) said Government borrowing hit £22.9 billion, the second highest June since records began in 1993.
It is £4.1 billion more than the same month a year ago, the ONS said.
Central Government spent £86 billion in June, an increase of £9 billion.
The rise came largely from a £10.3 billion jump in the amount of interest paid on Government loans.
“Today’s figures put paid to the idea that inflation is an effective tool for reducing debt,” said Michal Stelmach, senior economist at KPMG UK.
“The accrued debt interest in June is sufficient to fully offset the £18 billion expected yield from the income tax threshold freezes by 2025/26, which push people into higher tax brackets as their nominal incomes rise.”
But, Mr Stelmach added, a lot of the interest does not have to actually be paid yet.
Instead, the Government pays when its bonds mature.
The average length of a contract to come to maturity is 18 years.
The debt payments are linked to inflation, which has been soaring in recent months.
The cost of living has put extreme pressure on some households, as everyday items become more expensive.
The retail price index (RPI) soared to 11.1% in April – the month June’s interest payments are calculated on.
It was up from 2.9% a year earlier, in large part due to a 54% spike in average energy bills.
“The huge figure surely will be used by (Conservative Party leadership candidate Rishi) Sunak to argue that tax cuts must wait until after inflation has fallen back,” said Samuel Tombs, chief UK economist at Pantheon Macroeconomics.
“Indeed, RPI inflation likely will surge again in October, when the energy price cap will jump, boosting interest payments in December.”
Debt interest was actually lower than expected.
The Office for Budget responsibility had expected the payments to reach £19.7 billion, but the final future was £19.4 billion.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 